Acoustic Energy Conversion
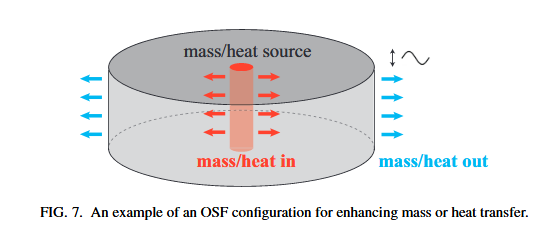
Sound waves, the periodic compression-expansion of a fluid in time and space, are `virtual pistons’ capable of performing useful work without the need for mechanical moving parts. We look at how these sound waves may be spontaneously excited and used for energy conversion, in applications such as refrigerators, compressors, and electrical generators.
Membrane Separation
Membrane Formation, Structure, and Performance
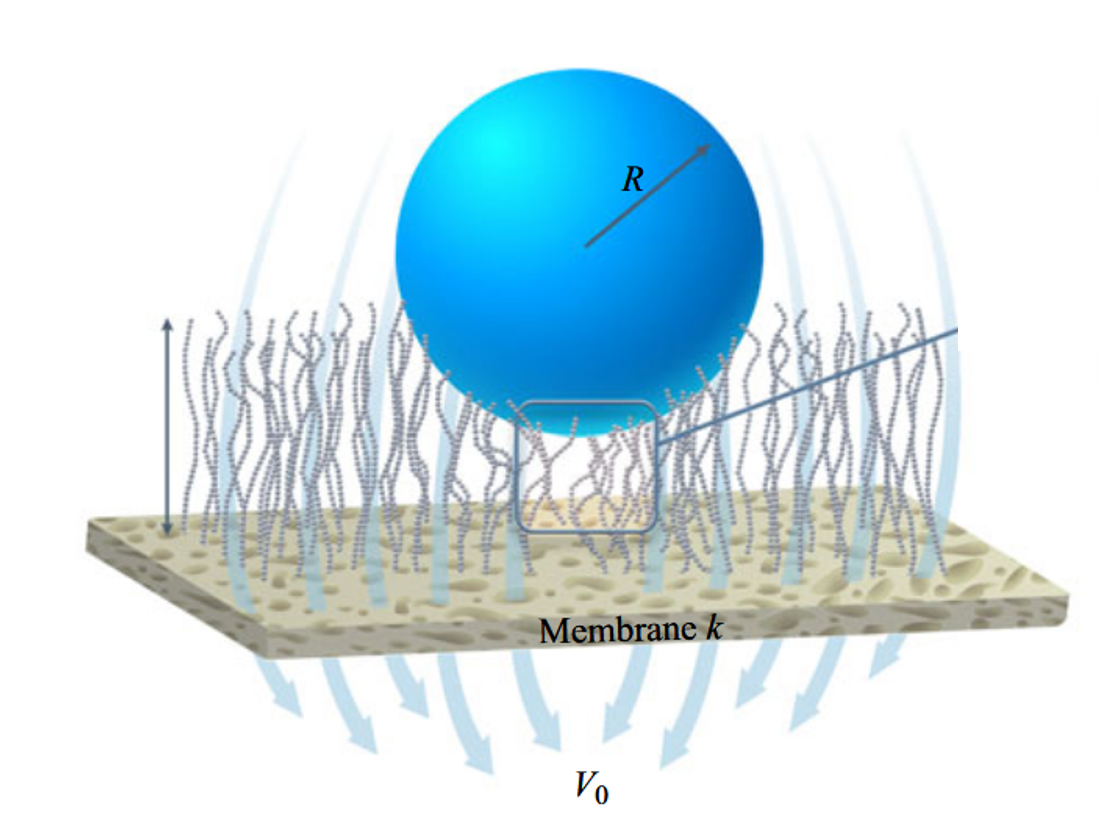
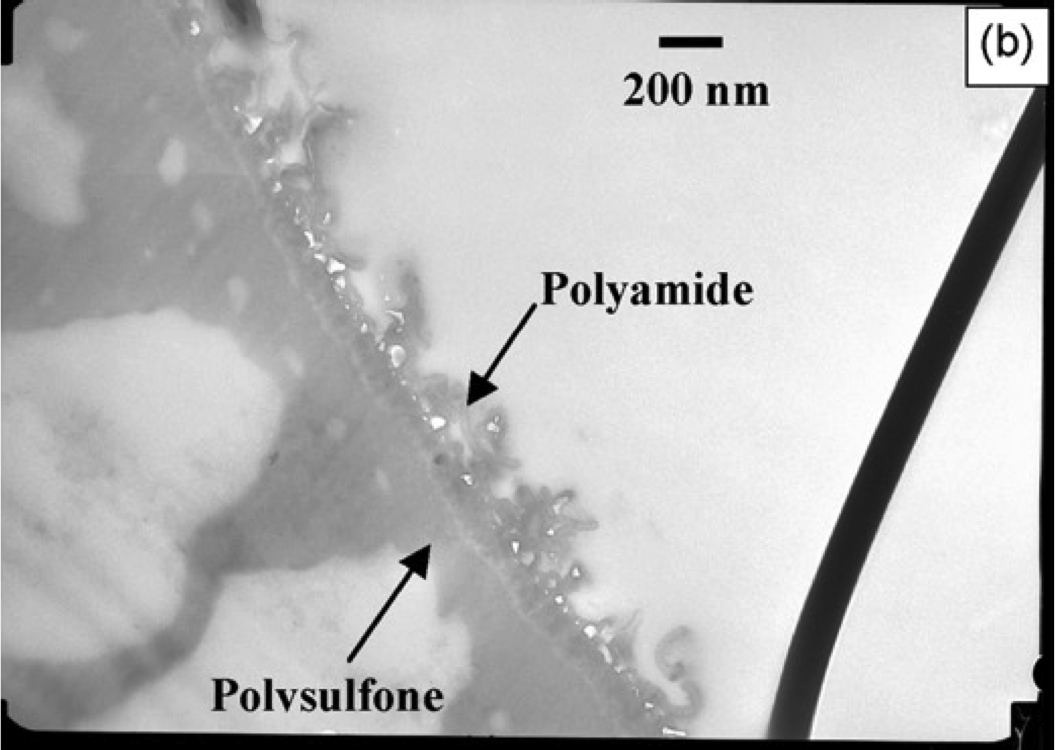
Transport of water and solutes through polymeric films is fundamental to the separation capacity of modern composite membranes, which comprise a thin film overlaying a porous support.
Membrane Fouling and Cleaning
Fouling of various origins – organic, colloidal, mineral or biological – is still a limiting factor in the large-scale application of membrane technology for water production. Our activities span a range of problems and fundamental questions related to fouling minimization.
Soft materials and interfaces
Biofilms and Flow
Biofilms are widely defined as bacteria consortia embedded in a self-secreted ‘gel’ matrix, primarily composed of polysaccharides and proteins. They may play a crucial role in both a positive and a negative manner. We use microfluidic channels combined with microscopy so as to probe the development of biofilms under flow conditions.
Microrheology on Membrane Surfaces
Soft materials are often the main components of biological and organic fouling. Complex behaviors arise from these materials when undergoing a fixed shear or stress. In our research, the soft material is analyzed when deposited on a semi-permeable surface.
VISIT US!